The latest capacitor manufacturer What are the procurement models of equipment components?
The Latest Capacitor Manufacturer - Procurement Models of Equipment Components
I. Introduction
The capacitor manufacturing industry plays a crucial role in the electronics sector, providing essential components for a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to industrial machinery. As technology advances and the demand for high-performance capacitors increases, manufacturers must adopt effective procurement models for their equipment components. This article explores the latest trends in capacitor manufacturing and the various procurement models that can enhance operational efficiency and product quality.
II. Understanding Capacitors
A. Definition and Function of Capacitors
Capacitors are passive electronic components that store and release electrical energy. They consist of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material known as a dielectric. When voltage is applied, an electric field forms across the dielectric, allowing the capacitor to store energy. Capacitors are essential for filtering, smoothing, and energy storage in electronic circuits.
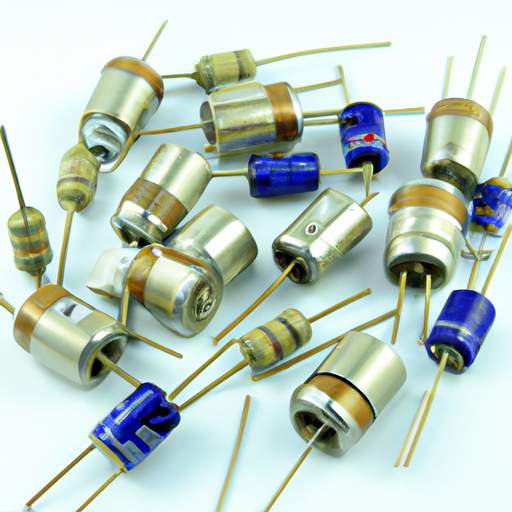
B. Types of Capacitors Commonly Used in Manufacturing
1. **Ceramic Capacitors**: Known for their small size and high reliability, ceramic capacitors are widely used in high-frequency applications. They are made from ceramic materials and are available in various capacitance values.
2. **Electrolytic Capacitors**: These capacitors are polarized and typically used for applications requiring high capacitance values. They are commonly found in power supply circuits.
3. **Film Capacitors**: Made from thin plastic films, these capacitors offer excellent stability and low losses, making them suitable for audio and high-frequency applications.
4. **Tantalum Capacitors**: Known for their high capacitance-to-volume ratio, tantalum capacitors are used in compact electronic devices. They are stable and reliable but can be more expensive than other types.
C. Applications of Capacitors in Various Industries
Capacitors are used in numerous applications, including power electronics, telecommunications, automotive systems, and consumer electronics. Their ability to store and release energy makes them vital for energy management, signal processing, and noise reduction in electronic circuits.
III. The Role of Equipment Components in Capacitor Manufacturing
A. Key Equipment Used in Capacitor Production
The production of capacitors involves several key pieces of equipment:
1. **Dielectric Material Processing Machines**: These machines are used to prepare and process the dielectric materials that form the core of capacitors.
2. **Winding and Stacking Equipment**: This equipment is essential for assembling the capacitor's internal structure, including winding the dielectric and conductive layers.
3. **Soldering and Assembly Machines**: These machines facilitate the assembly of capacitor components and ensure reliable electrical connections.
4. **Testing and Quality Control Equipment**: Quality assurance is critical in capacitor manufacturing. Testing equipment ensures that capacitors meet performance specifications and regulatory standards.
B. Importance of High-Quality Components for Efficiency and Reliability
The efficiency and reliability of capacitors depend significantly on the quality of the equipment components used in their production. High-quality components lead to better performance, reduced failure rates, and increased customer satisfaction.
IV. Procurement Models in Equipment Components
A. Definition of Procurement Models
Procurement models refer to the strategies and processes organizations use to acquire goods and services. In the context of capacitor manufacturing, these models are crucial for sourcing equipment components effectively.
B. Overview of Different Procurement Models
1. **Traditional Procurement**
- **Description and Characteristics**: This model involves a straightforward purchasing process, where manufacturers buy components from suppliers based on established contracts.
- **Advantages and Disadvantages**: While traditional procurement is simple, it may lack flexibility and responsiveness to market changes.
2. **Just-in-Time (JIT) Procurement**
- **Description and Characteristics**: JIT procurement focuses on minimizing inventory by ordering components only as needed.
- **Advantages and Disadvantages**: This model reduces holding costs but can lead to supply chain disruptions if suppliers cannot meet demand promptly.
3. **Strategic Sourcing**
- **Description and Characteristics**: Strategic sourcing involves a comprehensive analysis of suppliers and market conditions to optimize procurement decisions.
- **Advantages and Disadvantages**: This model can lead to cost savings and improved supplier relationships but requires significant time and resources.
4. **E-Procurement**
- **Description and Characteristics**: E-procurement utilizes digital platforms to streamline the purchasing process, allowing for greater efficiency and transparency.
- **Advantages and Disadvantages**: While e-procurement can reduce administrative costs, it may require initial investments in technology.
5. **Collaborative Procurement**
- **Description and Characteristics**: This model involves multiple organizations working together to procure goods and services, leveraging collective buying power.
- **Advantages and Disadvantages**: Collaborative procurement can lead to cost savings but may require complex coordination among participants.
V. Factors Influencing Procurement Decisions
Several factors influence procurement decisions in capacitor manufacturing:
A. Cost Considerations
Manufacturers must balance the cost of components with their quality and reliability. Lower costs may lead to compromised quality, impacting overall performance.
B. Quality and Reliability of Components
High-quality components are essential for producing reliable capacitors. Manufacturers must evaluate suppliers based on their ability to deliver consistent quality.
C. Supplier Relationships and Trust
Building strong relationships with suppliers fosters trust and collaboration, which can lead to better pricing, improved service, and enhanced innovation.
D. Lead Times and Delivery Schedules
Timely delivery of components is critical for maintaining production schedules. Manufacturers must consider lead times when selecting suppliers.
E. Technological Advancements and Innovations
Staying abreast of technological advancements can help manufacturers identify new procurement opportunities and improve their production processes.
VI. Case Studies of Successful Procurement Models in Capacitor Manufacturing
A. Example 1: A Leading Capacitor Manufacturer Using JIT Procurement
A prominent capacitor manufacturer implemented a JIT procurement model, significantly reducing inventory costs and improving cash flow. By closely collaborating with suppliers, they ensured timely deliveries, allowing for a more agile production process.
B. Example 2: A Manufacturer Leveraging Strategic Sourcing for Cost Efficiency
Another manufacturer adopted strategic sourcing to analyze their supply chain and negotiate better terms with suppliers. This approach led to substantial cost savings and improved supplier performance.
C. Example 3: An Innovative Approach Through E-Procurement
A forward-thinking capacitor manufacturer embraced e-procurement, streamlining their purchasing process and enhancing transparency. This model allowed them to quickly adapt to market changes and improve supplier collaboration.
VII. Challenges in Procurement for Capacitor Manufacturers
A. Supply Chain Disruptions
Global events, such as pandemics or geopolitical tensions, can disrupt supply chains, affecting the availability of critical components.
B. Fluctuating Material Costs
Volatile material prices can impact procurement budgets, making it challenging for manufacturers to maintain profitability.
C. Regulatory Compliance and Standards
Manufacturers must navigate complex regulatory environments, ensuring that their components meet industry standards and compliance requirements.
D. Managing Supplier Relationships
Maintaining strong relationships with suppliers is essential for ensuring consistent quality and timely deliveries. However, managing these relationships can be challenging, especially in a competitive market.
VIII. Future Trends in Procurement Models for Capacitor Manufacturing
A. Increasing Reliance on Technology and Automation
The future of procurement in capacitor manufacturing will likely see increased reliance on technology and automation, streamlining processes and enhancing efficiency.
B. Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Procurement Practices
As environmental concerns grow, manufacturers will need to adopt sustainable procurement practices, focusing on eco-friendly materials and processes.
C. The Rise of Digital Platforms for Procurement
Digital platforms will continue to transform procurement, offering manufacturers greater visibility and control over their supply chains.
D. Globalization and Its Impact on Procurement Strategies
Globalization will influence procurement strategies, as manufacturers seek to source components from diverse markets to mitigate risks and reduce costs.
IX. Conclusion
In conclusion, procurement models play a vital role in the capacitor manufacturing industry, influencing efficiency, quality, and overall competitiveness. As manufacturers navigate the complexities of the supply chain, they must evaluate and adapt their procurement strategies to meet the demands of a rapidly changing market. By embracing innovative approaches and leveraging technology, capacitor manufacturers can position themselves for success in the future.
X. References
A comprehensive list of academic papers, industry reports, and relevant literature on procurement models and capacitor manufacturing would be included here to support the insights presented in this article.
---
This blog post provides a detailed exploration of the latest trends in capacitor manufacturing and the various procurement models that can enhance operational efficiency and product quality. By understanding these dynamics, manufacturers can make informed decisions that drive success in a competitive landscape.